Applications
SCADA systems are used in various industries, including:
- Power generation and distribution:Monitoring and controlling power grids.
- Oil and gas:Monitoring and controlling pipelines, refineries, and other facilities.
- Water and wastewater treatment:Monitoring and controlling water supply and wastewater treatment plants.
- Manufacturing:Monitoring and controlling industrial processes in factories and other manufacturing facilities.
- Transportation:Monitoring and controlling traffic, rail, and other transportation systems.
Benefits
- Improved efficiency and productivity:
By automating tasks and providing real-time data, SCADA systems can improve efficiency and productivity.
By minimizing waste and optimizing processes, SCADA systems can reduce operating costs.
By providing real-time monitoring and control, SCADA systems can help ensure the safety of workers and the environment.
- Enhanced decision-making:
By providing real-time data and historical records, SCADA systems can help operators make better decisions.
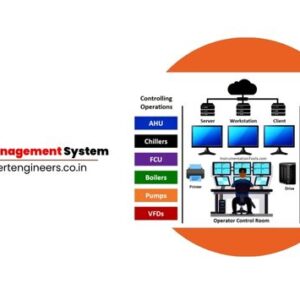
- SCADA System: What is it? (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition)






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.